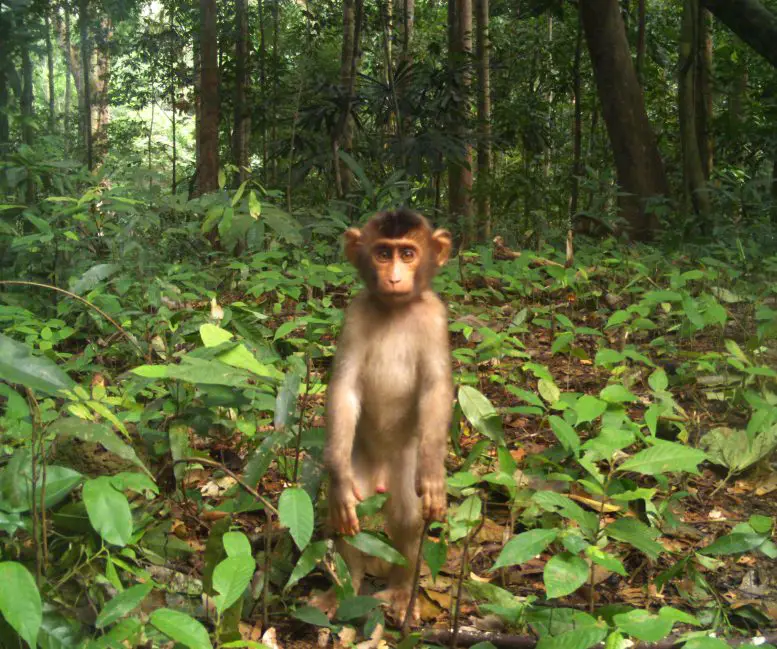

Human-driven habitat changes in Southeast Asia are causing wild pig and macaque population booms, threatening ecosystems and increasing disease risks. Above is a pig-tailed macaque baby in Malaysia. Credit: Ecological Cascades Lab
Rising numbers of wild pigs and macaque monkeys in Southeast Asia pose risks to native forests and could lead to disease spread among livestock and humans, reveals a study led by The University of Queensland.
Dr. Matthew Luskin, affiliated with UQ’s School of the Environment, alongside his team, gathered and assessed species population data from various parts of the region,
some of it collected with a network of cameras.
“Macaques and wild pigs are taking over Southeast Asia’s disturbed forests,” Dr Luskin said. “Humans are largely to blame for this by altering forests with logging and establishing palm oil farms which provide food and ideal breeding conditions for these animals. We saw that wild boar and macaque numbers were 400 percent higher in forests near the plantations than in untouched environments. These animals take full advantage of the farmland, raiding crops and thriving on calorie‐rich foods.”
Setting and monitoring the camera traps provided Dr. Luskin with an up-close experience of the exploding numbers.
“I encountered huge troops of macaques in Thailand, Malaysia, and Indonesia – they were everywhere in the forest edges, following us and interfering with our equipment,” Dr Luskin said. “At first it was frustrating but then was eerie as we became completely surrounded.”
Dr Luskin said there were significant human health risks in the rising pig and macaque populations.
“The wildlife origins of the COVID-19 pandemic show that mammals in human-modified ecosystems often host high pathogen loads and pose serious zoonotic disease risks,” he said. “Both pigs and macaques are recognized as carriers of diseases that can be transmitted to people and they’re the most common species in a region considered to be the global zoonotic disease hotspot.”
Collaborator, Professor Carlos Peres from the University of East Anglia (UK), said abnormally high populations of wildlife species that are disease reservoirs often occur in human-modified tropical forests.
“This study again shows that densely settled rural areas in Southeast Asia may be a source of future human epidemics,” he said.
University of East Anglia and Southern University of Science and Technology (China) PhD candidate, Jonathan Moore, said the immediate effects of the population explosions could be seen on native flora in the affected regions.
“Both pigs and macaques trigger negative cascading impacts in these pristine ecosystems,” Mr Moore said. “They kill the seeds and seedlings of native plants and eat bird and reptile eggs. The Malaysian pigs alone were found to reduce rainforest tree regeneration by 62 percent.”
The researchers say action is needed to minimize population expansions of wild pigs and macaques.
“Efforts to manage the populations of these species have failed in the past because of their rapid reproductive capacity and public outcry,” Dr Luskin said. “Nobody favors needless killing of wildlife but the negative social and ecological impacts from hyperabundant pest species do demand ethical and urgent management solutions.”
Reference: “The rise of hyperabundant native generalists threatens both humans and nature” by Jonathan H. Moore, Luke Gibson, Zachary Amir, Wirong Chanthorn, Abdul Hamid Ahmad, Patrick A. Jansen, Calebe P. Mendes, Manabu Onuma, Carlos A. Peres and Matthew Scott Luskin, 13 June 2023, Biological Reviews.
DOI: 10.1111/brv.12985







Be the first to comment on "“They Were Everywhere” – Exploding Monkey and Pig Populations Pose Human Disease Risk"